Solid particle removal process (II): Solid particle removal process
- Measurement and control standards of solid particles
Total suspended solids (TSS) is usually used as a parameter to measure solid particles in recirculating aquaculture. It mainly refers to the total amount of solid particles with a particle size greater than 1 micron in a unit of water. In the circulating water system, TSS includes fish feces, leftover bait, bioflocs (dead bacteria and live bacteria), etc. The size of these suspended particles varies greatly from micron to centimeter level. Suspended particles can directly affect the health and growth of fish (especially cold water fish), and increase the burden on the biofilter. Therefore, the concentration of suspended particles in the circulating water should be maintained within a reasonable range.
In some EU countries, the control of suspended particulate matter in recirculating aquaculture systems is relatively strict. For example, for water bodies used for recirculating aquaculture, the concentration of suspended particulate matter (measured by total suspended solids TSS) is usually expected to be controlled below 15 mg/L to maintain good water quality and ecological environment.
The United States also has relevant water quality regulations in the field of aquaculture and water treatment. In the recirculating aquaculture system, the corresponding suspended particulate matter content (converted through turbidity and other related indicators) is also subject to certain restrictions. The concentration of suspended particulate matter is generally around 8-12mg/L as a relatively ideal range to ensure the survival and reproduction of aquatic organisms.
In the actual operation of China 's factory-scale recirculating aquaculture systems, the suspended particulate matter concentration (SS) is generally required to be controlled below 10 mg/L. For the breeding of some precious species with high water quality requirements, such as salmon, it is even required to be controlled below 5 mg/L.
- Process for removing solid particles
The removal of solid particles is an important part of water treatment in a recirculating aquaculture system, and is usually the first step in water treatment. The core means of the solid particle removal process in a recirculating aquaculture is physical filtration. Through mechanical filtration, gravity separation and other methods, suspended particles, feed residues, fish feces and other solid substances in the water are intercepted and removed, thereby purifying the water quality. According to the size of the solid particles, the process of solid particle removal includes three process steps: pretreatment, coarse filtration and fine filtration.
1. Pretreatment
Pretreatment is mainly to remove larger particles with a particle size of more than 100μm, especially fish feces and leftover bait, to avoid them increasing the load of subsequent processes after they are broken in the system. The main process package is sedimentation. Sedimentation is a simple process technology of gravity separation. It is achieved through the following equipment:
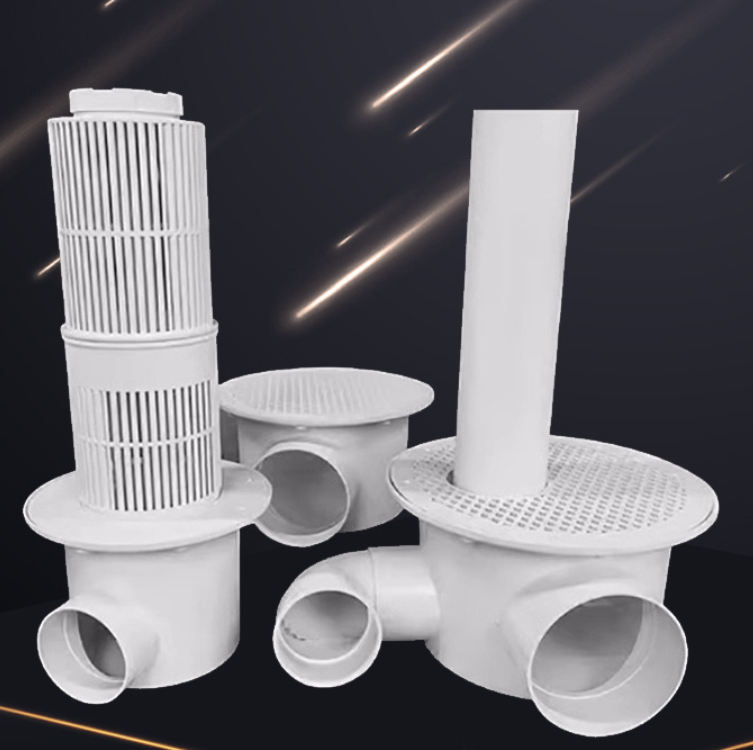
1. Sewage collector at the bottom of the breeding pond
A common sewage collector is a fish toilet. Fish toilets are usually installed at the bottom of the aquaculture pond. Through the action of rotating water flow, feces and leftover bait at the bottom of the pond are discharged. Fish toilets improve sewage collection efficiency, reduce the frequency of manual cleaning, and improve the stability of the aquaculture environment.
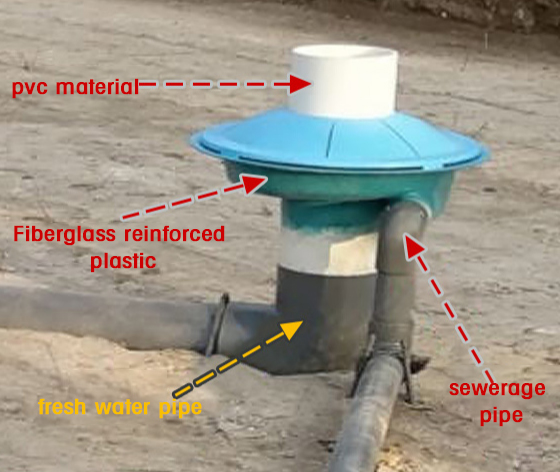

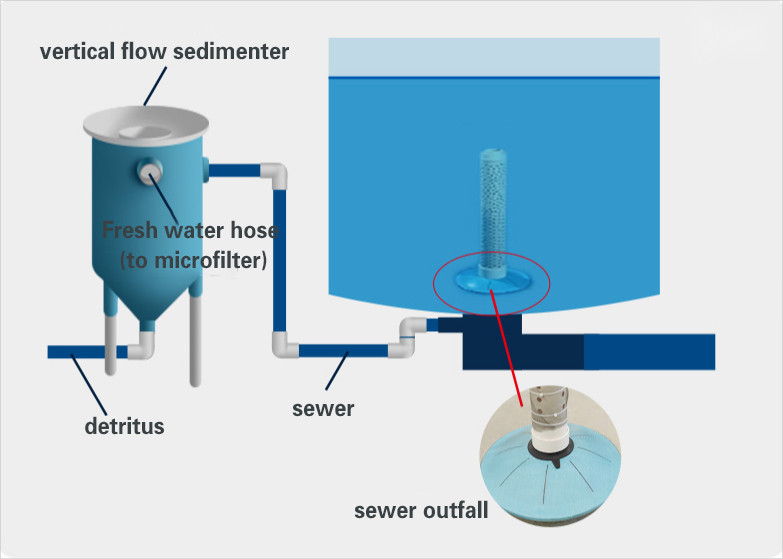
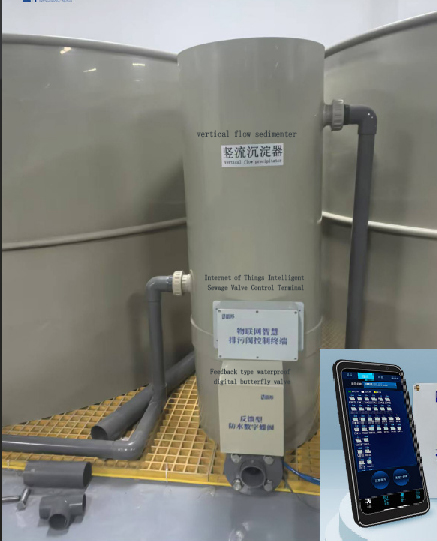
2. Vertical flow sedimentation tank
Vertical flow sedimentation tank uses the natural sedimentation principle of water flow under the action of gravity to separate suspended matter and particulate matter in water.
After the water flows into the separation chamber from the water inlet, the suspended solids and particles gradually settle to the bottom under the combined effect of gravity and water flow velocity, while the clean water is discharged from the upper outlet. The vertical flow sedimentator can remove 50%~70% of the solid particles in the settled particle dirt, which can greatly reduce the pressure of subsequent equipment.

3. Cornell Double Drainage System
Cornell double drainage mainly refers to a double drainage method used by Cornell University in fish pond design. This method is particularly suitable for circular fish ponds. Its basic feature is to combine bottom drainage with surface overflow technology. Two drainage outlets, bottom drainage and side drainage, are set on the fish pond to timely discharge settleable particles larger than 100 microns through the bottom drainage, thereby avoiding particles entering the microfiltration machine and causing secondary crushing. At the same time, suspended particles smaller than 100 microns are discharged into the microfiltration machine through the surface drainage for further filtration. In the Cornell double drainage system, 10%-25% of the water flows out through the bottom drain pipe, and 75%-90% of the water flows out through the side drainage. After gravity sedimentation through the bottom slow flow method, about 91% of the feces and 98% of the residual bait enter the vertical flow sedimentator through the bottom fish toilet and are discharged after sedimentation.

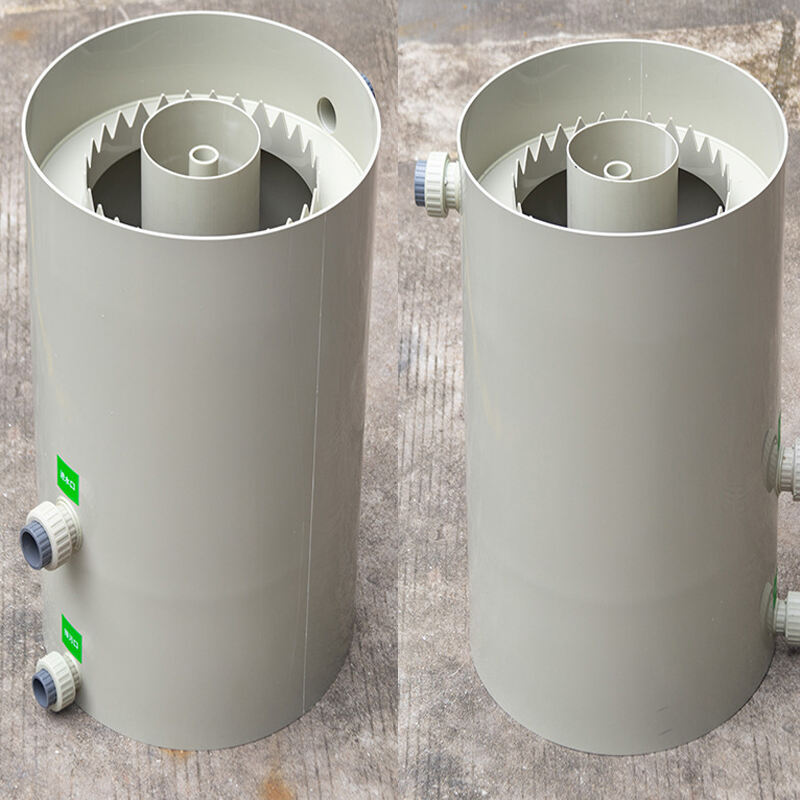
2.Coarse filtration
The purpose of coarse filtration is to remove suspended solid matter with a particle size of 30~100μm using conventional media filtration technology. The commonly used equipment is a rotary drum microfilter. The working principle of the microfilter is that after filtering through the microporous filter medium, clean water is discharged from the outlet pipe, while the trapped impurities are collected on the surface or inside the filter medium. The microfilter can remove 30%~50% of suspended solid particles.
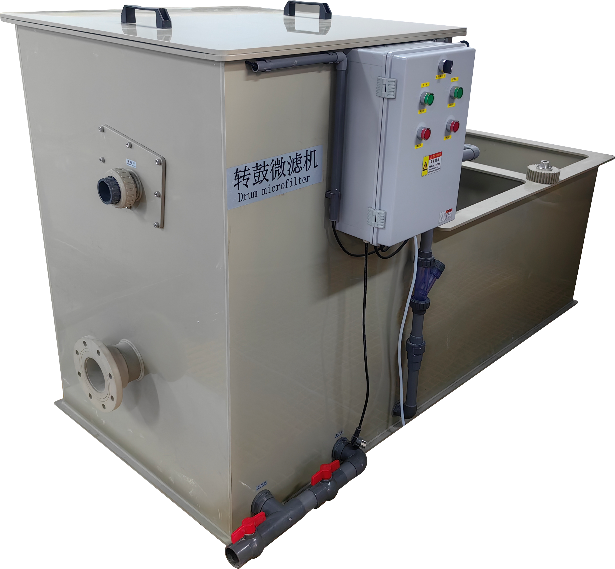

Drum Microfilter
3. Fine processing
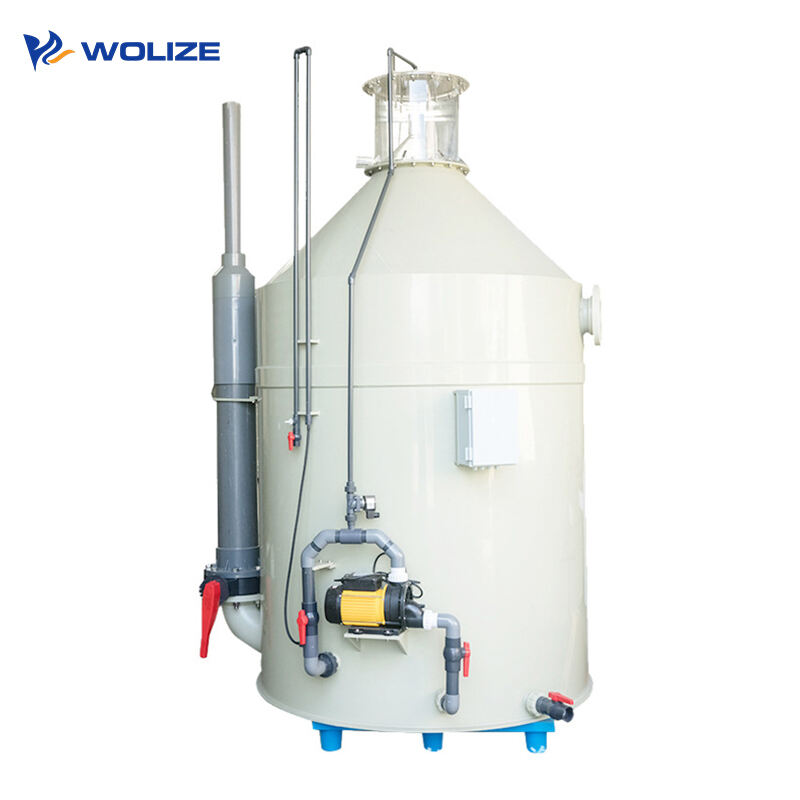
Fine treatment is mainly used to remove tiny suspended particles below 30μm and some soluble organic matter. It is mainly carried out by foam separation through protein skimmer. Foam separation is a common method that can remove tiny suspended particles and soluble organic matter, and also has certain functions of increasing oxygen and removing carbon dioxide.

Protein skimmer
Recommended Products
Hot News
-
The Christmas discount has arrived
2024-12-26
-
Is it true that raising fish in high-density canvas fish ponds is more efficient than ordinary ponds?
2024-12-16
-
Advantages of galvanized canvas fish pond
2024-10-14
-
High-density fish farming technology, fish pond cost, canvas fish pond, canvas pond, high-density fish farming
2024-10-12
-
Why choose flowing water high-density aquaculture
2023-11-20